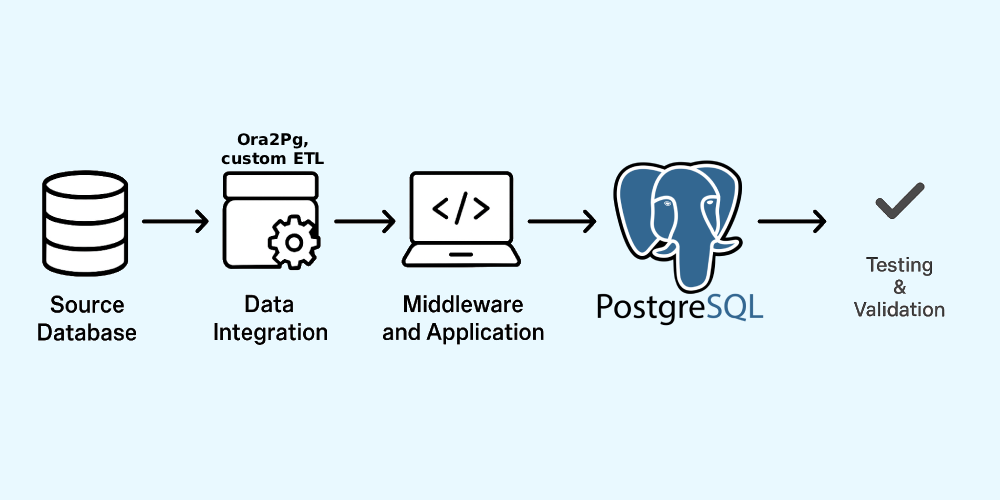
Migration Architecture
A successful migration begins with choosing the right architecture based on the organization's needs.
The migration architecture outlines the process of transitioning from a commercial relational database system like Oracle or SQL Server to an open-source alternative such as PostgreSQL. It begins with the source database, which contains the existing data, schema, and logic. A data integration layer; tools like Ora2Pg or custom ETL scripts is used to extract, transform, and load the data into PostgreSQL while handling differences in data types, syntax, and structures. The middleware and application layers are then adjusted to ensure that application code, database drivers, and ORM configurations are fully compatible with PostgreSQL. Finally, a thorough testing and validation layer ensures that data consistency, query performance, and application behavior remain intact.